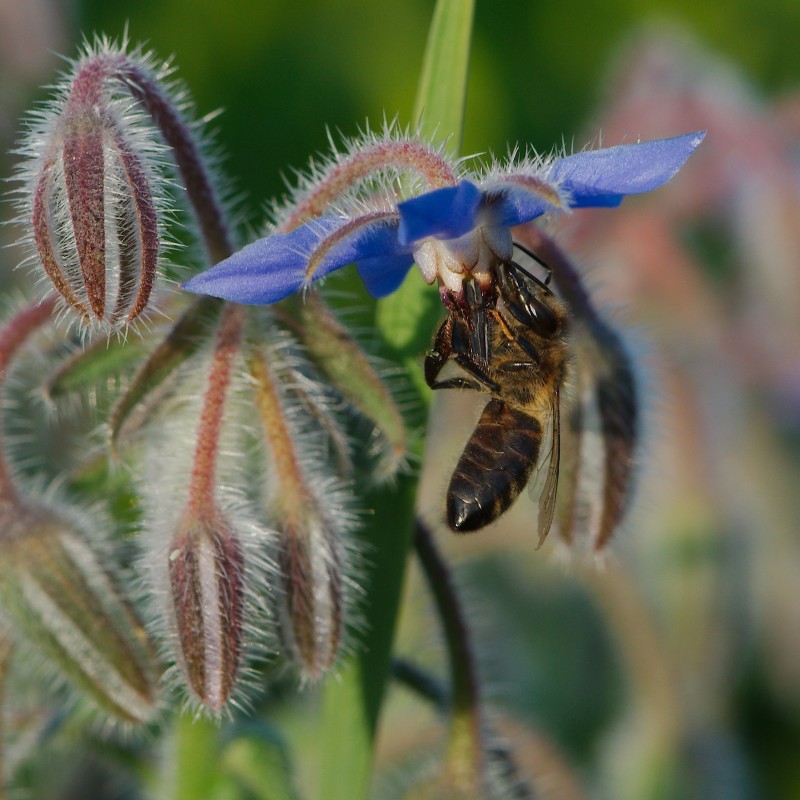








Borage (/ˈbʌrɪdʒ/ (About this soundlisten); Borago officinalis), also known as a starflower, is an annual herb in the flowering plant family Boraginaceae. It is native to the Mediterranean
Borage (/ˈbʌrɪdʒ/ (About this soundlisten); Borago officinalis), also known as a starflower, is an annual herb in the flowering plant family Boraginaceae. It is native to the Mediterranean region and has naturalized in many other locales. It grows satisfactorily in gardens in the UK climate, remaining in the garden from year to year by self-seeding. The leaves are edible and the plant is grown in gardens for that purpose in some parts of Europe. The plant is also commercially cultivated for borage seed oil extracted from its seeds. The plant contains pyrrolizidine alkaloids, some of which are hepatotoxic, mutagenic and carcinogenic (see below under Phytochemistry).
Description
Borago officinalis grows to a height of 60–100 cm (2.0–3.3 ft), and is bristly or hairy all over the stems and leaves; the leaves are alternate, simple, and 5–15 cm (2.0–5.9 in) long. The flowers are complete, perfect with five narrow, triangular-pointed petals. Flowers are most often blue, although pink flowers are sometimes observed. White flowered types are also cultivated. The blue flower is genetically dominant over the white flower.[3] The flowers arise along scorpioid cymes to form large floral displays with multiple flowers blooming simultaneously, suggesting that borage has a high degree of geitonogamy (intra-plant pollination).[3] It has an indeterminate growth habit which may lead to prolific spreading. In temperate climate such as in the UK, its flowering season is relatively long, from June to September. In milder climates, borage will bloom continuously for most of the year.
Characteristics and uses
Traditionally borage was cultivated for culinary and medicinal uses, although today commercial cultivation is mainly as an oilseed. Borage is used as either a fresh vegetable or a dried herb. As a fresh vegetable, borage, with a cucumber-like taste, is often used in salads or as a garnish. The flower has a sweet honey-like taste and is often used to decorate desserts and cocktails.
Food
Vegetable use of borage is common in Germany, in the Spanish regions of Aragon and Navarre, in the Greek island of Crete and in the northern Italian region of Liguria. Although often used in soups, one of the better known German borage recipes is the Green Sauce (Grüne Soße) made in Frankfurt. In Italian Liguria, borage is commonly used as a filling of the traditional pasta ravioli and pansoti. It is used to flavour pickled gherkins in Poland.
Beverage
Borage is traditionally used as a garnish in the Pimms Cup cocktail,[4] but is nowadays often replaced by a long sliver of cucumber peel or by mint. It is also one of the key botanicals in Gilpin's Westmorland Extra Dry Gin.
Phytochemistry
The seeds contain 26-38% of borage seed oil, of which 17-28% is gamma-linolenic acid (GLA), the richest known source. The oil also contains the fatty acids palmitic acid (10-11%), stearic acid (3.5-4.5%), oleic acid (16-20%), linoleic acid (35-38%), eicosenoic acid (3.5-5.5%), erucic acid (1.5-3.5%), and nervonic acid (1.5%). The oil is often marketed as "starflower oil" or "borage oil" for use as a GLA supplement, although healthy adults will typically produce ample GLA from dietary linoleic acid.
The leaves contain small amounts (2-10 ppm of dried herb) of the liver-toxic Pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PA) intermedine, lycopsamine, amabiline and supinine and the non-toxic saturated PA thesinine.[6] PAs are also present in borage seed oil, but may be removed by processing. The German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment has advised that honey from borage contains PAs, transferred to the honey through pollen collected at borage plants, and advise that commercial honey production could select for raw honey with limited PA content to prevent contamination.
Herbal medicine
Traditionally, Borago officinalis has been used in hyperactive gastrointestinal, respiratory and cardiovascular disorders, such as gastrointestinal (colic, cramps, diarrhea), airways (asthma, bronchitis), cardiovascular, (cardiotonic, antihypertensive and blood purifier), urinary (diuretic and kidney/bladder disorders).
One case of status epilepticus has been reported that was associated with borage oil ingestion.
A methanol extract of borage has shown strong amoebicidal activity in vitro. The 50% inhibitory concentration (LD50) of the extract against Entamoeba histolytica was 33 µg/mL.
In history
Pliny the Elder and Dioscorides say that borage was the "Nepenthe" mentioned in Homer, which caused forgetfulness when mixed with wine.
Francis Bacon thought that borage had "an excellent spirit to repress the fuliginous vapour of dusky melancholie." John Gerard's Herball mentions an old verse concerning the plant: "Ego Borago, Gaudia semper ago (I, Borage, bring always joys)". He states that "Those of our time do use the flowers in salads to exhilerate and make the mind glad. There be also many things made of these used everywhere for the comfort of the heart, for the driving away of sorrow and increasing the joy of the mind. The leaves and flowers of Borage put into wine make men and women glad and merry and drive away all sadness, dullness and melancholy, as Dioscorides and Pliny affirm. Syrup made of the flowers of Borage comfort the heart, purge melancholy and quiet the frantic and lunatic person. The leaves eaten raw engender good blood, especially in those that have been lately sick."
Companion planting
Borage is used in companion planting. It is said to protect or nurse legumes, spinach, brassicas, and even strawberries. It is also said to be a good companion plant to tomatoes because it confuses the mother moths of tomato hornworms or manduca looking for a place to lay their eggs. Claims that it improves tomato growth and makes them taste better remain unsubstantiated.
Data sheet
 Reviews (0)
Reviews (0)