







Azadirachta indica, also known as Neem, Nimtree, and Indian Lilac is a tree in the mahogany family Meliaceae. It is one of two species in the genus Azadirachta
Azadirachta indica, also known as Neem, Nimtree, and Indian Lilac is a tree in the mahogany family Meliaceae. It is one of two species in the genus Azadirachta, and is native to India and the Indian subcontinent including Nepal, Pakistan, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka. Typically growing in tropical and semi-tropical regions. Neem trees now also grow in islands in the southern part of Iran. Its fruits and seeds are the source of neem oil.
Description
Neem is a fast-growing tree that can reach a height of 15–20 metres (49–66 ft), rarely to 35–40 metres (115–131 ft). It is evergreen, but in severe drought it may shed most or nearly all of its leaves. The branches are wide and spreading. The fairly dense crown is roundish and may reach a diameter of 15–20 metres (49–66 ft) in old, free-standing specimens. The neem tree is very similar in appearance to its relative, the Chinaberry (Melia azedarach).
The opposite, pinnate leaves are 20–40 centimetres (7.9–15.7 in) long, with 20 to 31 medium to dark green leaflets about 3–8 centimetres (1.2–3.1 in) long. The terminal leaflet is often missing. The petioles are short.
The (white and fragrant) flowers are arranged in more-or-less drooping axillary panicles which are up to 25 centimetres (9.8 in) long. The inflorescences, which branch up to the third degree, bear from 150 to 250 flowers. An individual flower is 5–6 millimetres (0.20–0.24 in) long and 8–11 millimetres (0.31–0.43 in) wide. Protandrous, bisexual flowers and male flowers exist on the same individual tree.
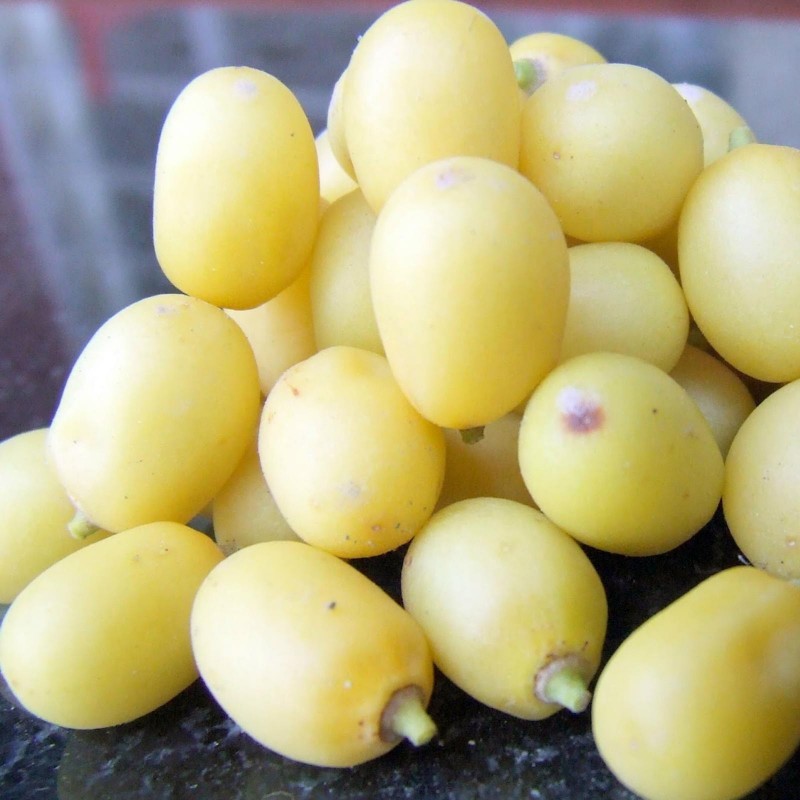
The fruit is a smooth (glabrous) olive-like drupe which varies in shape from elongate oval to nearly roundish, and when ripe is 1.4–2.8 centimetres (0.55–1.10 in) by 1.0–1.5 centimetres (0.39–0.59 in). The fruit skin (exocarp) is thin and the bitter-sweet pulp (mesocarp) is yellowish-white and very fibrous. The mesocarp is 0.3–0.5 centimetres (0.12–0.20 in) thick. The white, hard inner shell (endocarp) of the fruit encloses one, rarely two or three, elongated seeds (kernels) having a brown seed coat.
Uses
Neem leaves are dried in India and placed in cupboards to prevent insects eating the clothes and also while storing rice in tins.[9] Neem leaves are dried and burnt in the tropical regions to keep away mosquitoes.[citation needed] These flowers are also used in many Indian festivals like Ugadi. See below: #Association with Hindu festivals in India. As an ayurvedic herb, neem is also used in baths.
As a vegetable
The tender shoots and flowers of the neem tree are eaten as a vegetable in India. A souplike dish called Veppampoo charu (Tamil) (translated as "neem flower rasam") made of the flower of neem is prepared in Tamil Nadu. In West Bengal, young neem leaves are fried in oil with tiny pieces of eggplant (brinjal). The dish is called nim begun and is the first item during a Bengali meal that acts as an appetizer. It is eaten with rice.[
Neem is used in parts of mainland Southeast Asia, particularly in Cambodia aka sdov—ស្ដៅវ, Laos (where it is called kadao), Thailand (where it is known as sadao or sdao), Myanmar (where it is known as tamar) and Vietnam (where it is known as sầu đâu and is used to cook the salad gỏi sầu đâu). Even lightly cooked, the flavour is quite bitter and the food is not enjoyed by all inhabitants of these nations, though it is believed to be good for one's health. Neem gum is a rich source of protein. In Myanmar, young neem leaves and flower buds are boiled with tamarind fruit to soften its bitterness and eaten as a vegetable. Pickled neem leaves are also eaten with tomato and fish paste sauce in Myanmar.
Traditional medicinal use
Products made from neem trees have been used in India for over two millennia for their medicinal properties. Neem products are believed by Siddha and Ayurvedic practitioners to be anthelmintic, antifungal, antidiabetic, antibacterial, antiviral, contraceptive and sedative. It is considered a major component in siddha medicine and Ayurvedic and Unani medicine and is particularly prescribed for skin diseases. Neem oil is also used for healthy hair, to improve liver function, detoxify the blood, and balance blood sugar levels. Neem leaves have also been used to treat skin diseases like eczema, psoriasis, etc.
However, insufficient research has been done to assess the purported benefits of neem. In adults, short-term use of neem is safe, while long-term use may harm the kidneys or liver; in small children, neem oil is toxic and can lead to death. Neem may also cause miscarriages, infertility, and low blood sugar.
Other uses
The twigs are also used as tooth brush. One end is chewed to turn it into soft bristles to clean the teeth by brushing.
Toiletries: Neem oil is used for preparing cosmetics such as soap, shampoo, balms and creams as well as toothpaste.
Toothbrush: Traditionally, slender neem twigs (called datun;) are first chewed as a toothbrush and then split as a tongue cleaner.[19] This practise has been in use in India, Africa, and the Middle East for centuries. Many of India's 80% rural population still start their day with the chewing stick, while in urban areas neem toothpaste is preferred. Neem twigs are still collected and sold in markets for this use, and in rural India one often sees youngsters in the streets chewing on neem twigs. It has been found to be equally effective as a toothbrush in reducing plaque and gingival inflammation.[20][21]
Tree: Besides its use in traditional Indian medicine, the neem tree is of great importance for its anti-desertification properties and possibly as a good carbon dioxide sink.[citation needed]
Neem gum is used as a bulking agent and for the preparation of special purpose foods.
Neem blossoms are used in Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and Karnataka to prepare Ugadi pachhadi. A mixture of neem flowers and jaggery (or unrefined brown sugar) is prepared and offered to friends and relatives, symbolic of sweet and bitter events in the upcoming new year, Ugadi. "Bevina hoovina gojju" (a type of curry prepared with neem blossoms) is common in Karnataka throughout the year. Dried blossoms are used when fresh blossoms are not available. In Tamil Nadu, a rasam (veppam poo rasam) made with neem blossoms is a culinary specialty.
Cosmetics : Neem is perceived in India as a beauty aid. Powdered leaves are a major component of at least one widely used facial cream. Purified neem oil is also used in nail polish and other cosmetics.
Bird repellent: Neem leaf boiled in water can be used as a very cost effective bird repellent, especially for sparrows.
Lubricant : Neem oil is non drying and it resists degradation better than most vegetable oils. In rural India, it is commonly used to grease cart wheels.
Fertilizer : Neem has demonstrated considerable potential as a fertilizer. Neem cake is widely used to fertilize cash crops, particularly sugarcane and vegetables. Ploughed into the soil, it protects plant roots from nematodes and white ants, probably as it contains the residual limonoids.[citation needed] In Karnataka, people grow the tree mainly for its green leaves and twigs, which they puddle into flooded rice fields before the rice seedlings are transplanted.
Resin : An exudate can be tapped from the trunk by wounding the bark. This high protein material is not a substitute for polysaccharide gum, such as gum arabic. It may however, have a potential as a food additive, and it is widely used in South Asia as "Neem glue".
Bark : Neem bark contains 14% tannin, an amount similar to that in conventional tannin yielding trees (such as Acacia decurrens). Moreover, it yields a strong, coarse fibre commonly woven into ropes in the villages of India.
Honey : In parts of Asia neem honey commands premium prices, and people promote apiculture by planting neem trees.
Soap : 80% of India's supply of neem oil is now used by neem oil soap manufacturers.[22] Although much of it goes to small scale speciality soaps, often using cold-pressed oil, large scale producers also use it, mainly because it is cheap. Additionally it is antibacterial and antifungal, soothing and moisturising. It can be made with up to 40% neem oil.[22] Well known brands include Margo. Generally, the crude oil is used to produce coarse laundry soaps.
Against pox viruses : In Tamil Nadu, people who are affected with pox viruses are generally made to lie in bed made of neem leaves and branches. This prevents the spreading of pox virus to others and has been in practice since early centuries.
Etymology
Neem is a Hindi noun derived from Sanskrit Nimba.
Ecology
The neem tree is noted for its drought resistance. Normally it thrives in areas with sub-arid to sub-humid conditions, with an annual rainfall 400–1,200 millimetres (16–47 in). It can grow in regions with an annual rainfall below 400 mm, but in such cases it depends largely on ground water levels. Neem can grow in many different types of soil, but it thrives best on well drained deep and sandy soils. It is a typical tropical to subtropical tree and exists at annual mean temperatures between 21–32 °C (70–90 °F). It can tolerate high to very high temperatures and does not tolerate temperature below 4 °C (39 °F). Neem is one of a very few shade-giving trees that thrive in drought-prone areas e.g. the dry coastal, southern districts of India and Pakistan. The trees are not at all delicate about water quality and thrive on the merest trickle of water, whatever the quality. In India and tropical countries where the Indian diaspora has reached, it is very common to see neem trees used for shade lining streets, around temples, schools & other such public buildings or in most people's back yards. In very dry areas the trees are planted on large tracts of land.
Weed status
Neem is considered a weed in many areas, including some parts of the Middle East, most of Sub-Saharan Africa including West Africa and Indian Ocean states, and some parts of Australia. Ecologically, it survives well in similar environments to its own, but its weed potential has not been fully assessed.
In April 2015, A. indica was declared a class B and C weed in the Northern Territory, Australia, meaning its growth and spread must be controlled and plants or propagules are not allowed to be brought into the NT. It is illegal to buy, sell, or transport the plants or seeds. Its declaration as a weed came in response to its invasion of waterways in the "Top End" of the territory.
After being introduced into Australia, possibly in the 1940s, A. indica was originally planted in the Northern Territory to provide shade for cattle. Trial plantations were established between the 1960s and 1980s in Darwin, Queensland, and Western Australia, but the Australian neem industry did not prove viable. The tree has now spread into the savanna, particularly around waterways, and naturalised populations exist in several areas.
Chemical compounds
Ayurveda was the first to bring the anthelmintic, antifungal, antibacterial, and antiviral constituents of the Neem tree to the attention of natural products chemists. The process of extracting neem oil involves extracting the water insoluble components with ether, petrol ether, ethyl acetate and dilute alcohol. The provisional naming was nimbin (sulphur-free crystalline product with melting point at 205 °C, empirical composition C7H10O2), nimbinin (with similar principle, melting at 192 °C), and nimbidin (cream-coloured containing amorphous sulphur, melting at 90–100 °C). Siddiqui identified nimbidin as the main active antibacterial ingredient, and the highest yielding bitter component in the neem oil. These compounds are stable and found in substantial quantities in the Neem. They also serve as natural insecticides.
Neem coated urea is being used an alternate to plain urea fertilizer in India. It reduces pollution, improves fertilizer's efficacy and soil health.
Opis
 Reviews (0)
Reviews (0)