- -15%










|
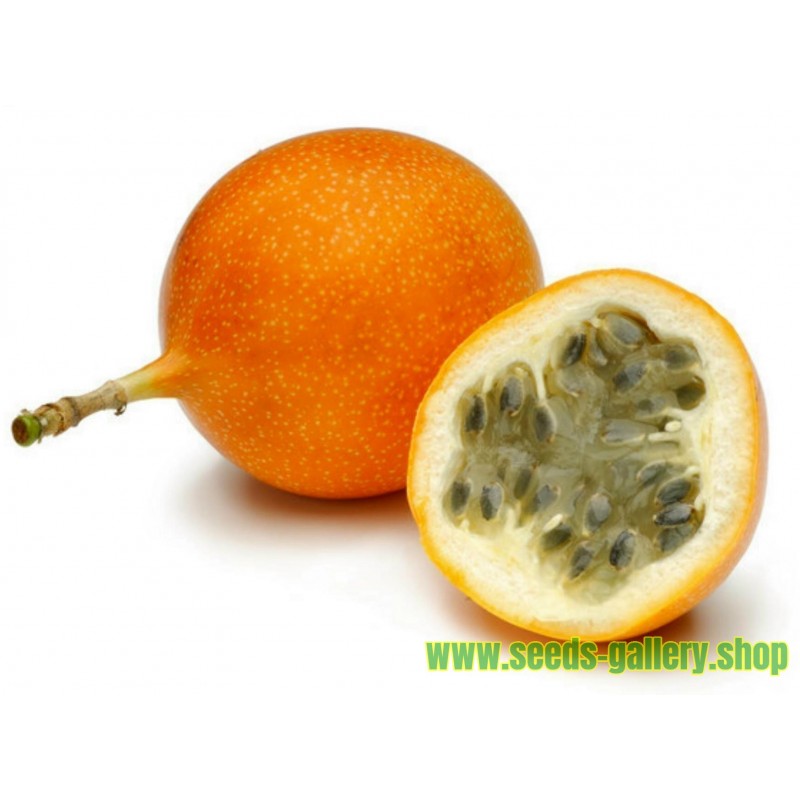
Sowing Instructions |
|
|
Propagation: |
Seeds / Cuttings |
|
Pretreat: |
about 24-48 hours soak in warm water |
|
Stratification: |
0 |
|
Sowing Time: |
all year round |
|
Sowing Depth: |
0.5 cm |
|
Sowing Mix: |
Coir or sowing mix + sand or perlite |
|
Germination temperature: |
25 ° C + |
|
Location: |
bright + keep constantly moist not wet |
|
Germination Time: |
2-4 Weeks |
|
Watering: |
Water regularly during the growing season |
|
|
|
 Reviews (0)
Reviews (0)