- -15%

Varietate din Rusia

Planta rezistenta la frig si inghet
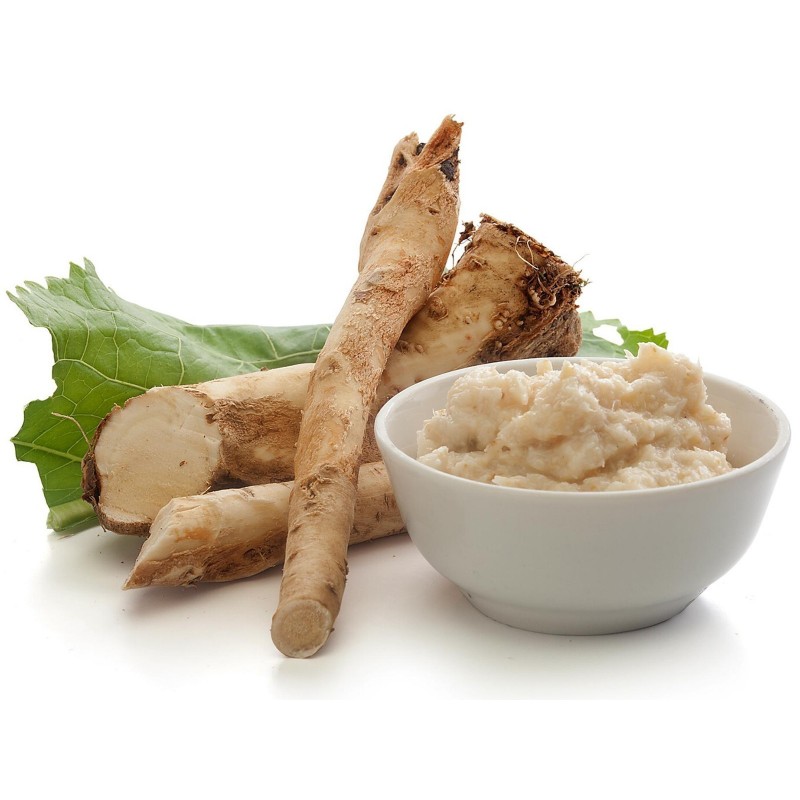













Horseradish (Armoracia rusticana, syn. Cochlearia armoracia) is a perennial plant of the Brassicaceae family (which also includes mustard, wasabi, broccoli, and cabbage).
Horseradish (Armoracia rusticana, syn. Cochlearia armoracia) is a perennial plant of the Brassicaceae family (which also includes mustard, wasabi, broccoli, and cabbage). It is a root vegetable used as a spice.
The plant is probably native to southeastern Europe and western Asia. It is popular worldwide. It grows up to 1.5 meters (4.9 feet) tall, and is cultivated primarily for its large, white, tapered root.
The intact horseradish root has hardly any aroma. When cut or grated enzymes from the now-broken plant cells break down sinigrin (a glucosinolate) to produce allyl isothiocyanate (mustard oil), which irritates the mucous membranes of the sinuses and eyes. Grated mash should be used immediately or preserved in vinegar for best flavor. Once exposed to air or heat it will begin to lose its pungency, darken in color, and become unpleasantly bitter tasting over time.
Horseradish is probably indigenous to temperate Eastern Europe, where its Slavic name chren seemed to Augustin Pyramus de Candolle more primitive than any Western synonym. Horseradish has been cultivated since antiquity.[6] According to Greek mythology, the Delphic Oracle told Apollo that the horseradish was worth its weight in gold. Dioscorides listed horseradish equally as Persicon sinapi (Diosc. 2.186) or Sinapi persicum (Diosc. 2.168),[8] which Pliny's Natural History reported as Persicon napy;[9] Cato discusses the plant in his treatises on agriculture, and a mural in Pompeii shows the plant. Horseradish is probably the plant mentioned by Pliny the Elder in his Natural History under the name of Amoracia, and recommended by him for its medicinal qualities, and possibly the wild radish, or raphanos agrios of the Greeks. The early Renaissance herbalists Pietro Andrea Mattioli and John Gerard showed it under Raphanus.[10] Its modern Linnaean genus Armoracia was first applied to it by Heinrich Bernhard Ruppius, in his Flora Jenensis, 1745, but Linnaeus himself called it Coclearia armoracia.
Both root and leaves were used as a medicine during the Middle Ages. The root was used as a condiment on meats in Germany, Scandinavia, and Britain. It was introduced to North America during European colonialization;[11] both George Washington and Thomas Jefferson mention horseradish in garden accounts.
William Turner mentions horseradish as Red Cole in his "Herbal" (1551–1568), but not as a condiment. In The Herball, or Generall Historie of Plantes (1597), John Gerard describes it under the name of raphanus rusticanus, stating that it occurs wild in several parts of England. After referring to its medicinal uses, he says:
The Horse Radish stamped with a little vinegar put thereto, is commonly used among the Germans for sauce to eat fish with and such like meats as we do mustard.
The word horseradish is attested in English from the 1590s. It combines the word horse (formerly used in a figurative sense to mean strong or coarse) and the word radish.
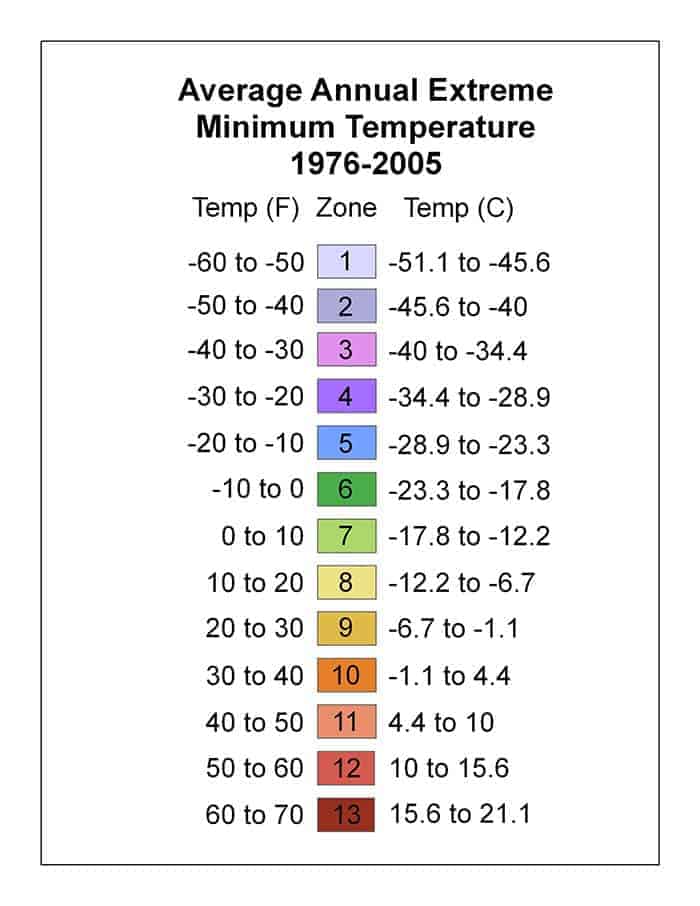
Horseradish is perennial in hardiness zones 2–9 and can be grown as an annual in other zones, although not as successfully as in zones with both a long growing season and winter temperatures cold enough to ensure plant dormancy. After the first frost in autumn kills the leaves, the root is dug and divided. The main root is harvested and one or more large offshoots of the main root are replanted to produce next year's crop. Horseradish left undisturbed in the garden spreads via underground shoots and can become invasive. Older roots left in the ground become woody, after which they are no longer culinarily useful, although older plants can be dug and re-divided to start new plants.[11][15] The early season leaves can be distinctively different, asymmetric spiky, before the mature typical flat broad leaves start to be developed.
The distinctive pungent taste of horseradish is from the compound allyl isothiocyanate. Upon crushing the flesh of horseradish, the enzyme myrosinase is released and acts on the glucosinolates sinigrin and gluconasturtiin, which are precursors to the allyl isothiocyanate. The allyl isothiocyanate serves the plant as a natural defense against herbivores. Since allyl isothiocyanate is harmful to the plant itself, it is stored in the harmless form of the glucosinolate, separate from the myrosinase enzyme. When an animal chews the plant, the allyl isothiocyanate is released, repelling the animal. Allyl isothiocyanate is an unstable compound, degrading over the course of days at 37 °C (99 °F). Because of this instability, horseradish sauces lack the pungency of the freshly crushed roots.
Cooks use the terms "horseradish" or "prepared horseradish" to refer to the grated root of the horseradish plant mixed with vinegar. Prepared horseradish is white to creamy-beige in color. It can be stored for months under refrigeration, but eventually will darken, indicating it is losing flavour and should be replaced. The leaves of the plant, while edible, are not commonly eaten, and are referred to as "horseradish greens", which have a flavor similar to that of the roots.
Horseradish sauce made from grated horseradish root and vinegar is a popular condiment in the United Kingdom and in Poland.[19] In the UK, it is usually served with roast beef, often as part of a traditional Sunday roast; but can be used in a number of other dishes also, including sandwiches or salads. A variation of horseradish sauce, which in some cases may substitute the vinegar with other products like lemon juice or citric acid, is known in Germany as Tafelmeerrettich. Also popular in the UK is Tewkesbury mustard, a blend of mustard and grated horseradish originating in medieval times and mentioned by Shakespeare (Falstaff says: "his wit's as thick as Tewkesbury Mustard" in Henry IV Part II[20]). A very similar mustard, called Krensenf or Meerrettichsenf, is popular in Austria and parts of Eastern Germany.[citation needed] In France, sauce au raifort is popular in Alsatian cuisine.[citation needed] In Russia horseradish root is usually mixed with grated garlic and small amount of tomatoes for color.
In the US the term "horseradish sauce" refers to grated horseradish combined with mayonnaise or salad dressing. Prepared horseradish is a common ingredient in Bloody Mary cocktails and in cocktail sauce, and is used as a sauce or sandwich spread. Horseradish cream is a mixture of horseradish and sour cream and is served alongside au jus for a prime rib dinner.
In Central and Eastern Europe horseradish is called khren (in various spellings like kren) in many Slavic languages, in Austria, in parts of Germany (where the other German name Meerrettich isn't used), in North-East Italy, and in Yiddish (כריין transliterated as khreyn).
There are two varieties of khreyn. "Red" khreyn is mixed with red beetroot and "white" khreyn contains no beetroot. It is popular in Ukraine (under the name of хрін, khrin), in Belarus (under the name of хрэн, chren), in Poland (under the name of chrzan), in the Czech Republic (křen), in Russia (хрен, khren), in Hungary (torma), in Romania (hrean), in Lithuania (krienai), in Bulgaria (хрян, khryan), and in Slovakia (under the name of chren). Having this on the table is a part of Christian Easter and Jewish Passover tradition in Eastern and Central Europe.
In parts of Southern Germany like Franconia, "Kren" is an essential component of the traditional wedding dinner. It is served with cooked beef and a dip made from lingonberry to balance the slight hotness of the Kren.
In Poland, a variety with red beetroot is called ćwikła z chrzanem or simply ćwikła.
In Ashkenazi European Jewish cooking beetroot horseradish is commonly served with gefilte fish.
In Transylvania and other Romanian regions, Red beetroot with horseradish is also used as a salad served with lamb dishes at Easter called sfecla cu hrean.
In Serbia, ren is an essential condiment with cooked meat and freshly roasted suckling pig.
In Croatia, freshly grated horseradish (Croatian: Hren) is often eaten with boiled ham or beef.
In Slovenia, and in the adjacent Italian regions of Friuli Venezia Giulia and nearby Italian region of Veneto, horseradish (often grated and mixed with sour cream, vinegar, hard-boiled eggs, or apples) is also a traditional Easter dish.
Further west in the Italian regions of Lombardy, Emilia-Romagna, and Piedmont, it is called "barbaforte (strong beard)" and is a traditional accompaniment to bollito misto; while in north-eastern regions like Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, Veneto and Friuli-Venezia Giulia, it is still called "kren" or "cren". In the southern region of Basilicata it is known as "rafano" and used for the preparation of the so-called "rafanata", a main course made of horseradish, eggs, cheese and sausage.
Horseradish is also used as a main ingredient for soups. In the Polish region of Silesia, horseradish soup is a common Easter Day dish.
The Japanese condiment wasabi, although traditionally prepared from the wasabi plant, is now usually made with horseradish due to the scarcity of the wasabi plant.[27] The Japanese botanical name for horseradish is seiyōwasabi (セイヨウワサビ, 西洋山葵), or "Western wasabi". Both plants are members of the family Brassicaceae.
In a 100 gram amount, prepared horseradish provides 48 calories and has high content of vitamin C with moderate content of sodium, folate and dietary fiber, while other essential nutrients are negligible in content. In a typical serving of one tablespoon (15 grams), horseradish supplies no significant nutrient content.
Horseradish contains volatile oils, notably mustard oil, and allyl isothiocyanate.
The enzyme horseradish peroxidase (HRP), found in the plant, is used extensively in molecular biology and biochemistry primarily for its ability to amplify a weak signal and increase detectability of a target molecule. HRP has been used in decades of research to visualize under microscopy and assess non-quantitatively the permeability of capillaries, particularly those of the brain.
For first season harvests, start the seeds indoors in January to February and transplant out in April. The goal is to achieve large, fully established roots that can be divided and/or replanted. If time is not pressing, direct sow any time from March into summer. Optimal soil temperature: 7-23°C (45-75°F).
Sow seeds 5mm-1cm (¼-½”) deep in well cultivated, deep soiil. Seeds will sprout in 7-25 days, depending on conditions. Thin or transplant to 20cm (8″) apart in rows 40-50cm (16-20″) apart.
Ideal pH: 6.0-6.8. Well drained, warm soil in full sun is best. Raised beds help with both drainage and warmth. Use 1 cup of complete organic fertilizer for every 3m (10′) of row. Newly emerged leaves are edible, or should be left to mature if growing for the roots. The flower petals are also edible — flowers should be removed before they set seeds, as they will self-sow with enthusiasm.
For the leaves, harvest as needed, shortly after they emerge, before they become woody. For the roots, harvest November through March. The roots can also be lifted and stored for spring planting to keep the crop going from season to season.
In our experience, insects do not cause problems for horseradish.
Horseradish is thought to repel aphids and whiteflies, blister beetles, potato beetles, and some varieties of caterpillar. Its flowers attract beneficial predatory hoverflies.
Fisa tehnica
Radishes are a hardy, easy-to-grow root vegetable that can be planted multiple times in a growing season.
Here’s how to plant and grow radishes in your garden!
Radish seeds can be planted in both the spring and the fall, but growth should be suspended in the height of summer when temperatures are typically too hot. (Hot temperatures may cause radishes to bolt, making them essentially useless.)
Otherwise, radishes are one of the easiest vegetables to grow.
Plant in a sunny spot. If radishes are planted in too much shade—or even where neighboring vegetable plants shade them—they will put all their energy into producing larger leaves.
Like carrots, radish plants are primarily grown for their roots. Though the soil needs to be rich in organic matter, it should not be compacted. If your soil is more clay-like, mix in some sand to loosen it and improve drainage.
If your soil isn’t rich in organic matter, incorporate a few inches of aged compost or all-purpose fertilizer (see packaging for amount) into the planting site as soon as the soil is workable.
Till your garden bed to remove any rocks or dirt clods before planting.
Practice three-year crop rotation. In other words, only plant radishes in the same spot every third year. This will help prevent diseases from affecting your crop.
For a spring planting, sow seeds 4–6 weeks before the average date of the last frost. See local frost dates here.
It’s best to plant radish seeds directly in the garden so as not to disturb their roots. Directly sow seeds outdoors 2 cm deep and 2,5 cm apart in rows 28 cm apart.
Plant another round of seeds every 10 days or so—while weather is still cool—for a continuous harvest of radishes in the late spring and early summer.
Plan on a fall planting. You can plant radishes later than any other root crop in late summer or early fall and still get a harvest. Sow seeds 4–6 weeks before the first fall frost.
Thin radishes to about 2 inches apart when the plants are a week old. Crowded plants do not grow well.
Consistent, even moisture is key. Keep soil evenly moist but not waterlogged. A drip irrigation system is a great way to achieve this.
Putting a thin layer of mulch around the radishes can help retain moisture in dry conditions.
Radishes will be ready to harvest quite rapidly, as soon as three weeks after planting for some varieties.
For most varieties, harvest when roots are approximately 2,5 cm in diameter at the soil surface. Pull one out and test it before harvesting the rest!
Do not leave radishes in the ground long after their mature stage; their condition will deteriorate quickly.
Cut the tops and the thin root tail off, wash the radishes, and dry them thoroughly. Store in plastic bags in the refrigerator.
Radish greens can be stored separately for up to three days.
Radish seeds have a fairly long shelf life. Don’t be afraid to plant radish seeds that are up to five years old. All may not germinate, but you’ll have plenty that will.
 Reviews (4)
Reviews (4)




Hallo habe 5 Samen bekommen und 3 sind auf gegangen ich freue mich vielen Dank!
Excellent seeds, all have sprout and grow strongly. Great service, rapidly arrived. Will buy again if I have to. Thank you
Received pack of 10 seeds today a little bit before time.This must be due to attentive sender and efficient postal system.The real test now falls to me to try to germinate ,transplant, and successfully grow even just one of the resulting plants and then I will be in a position to award even more stars.Thanks, from,Jerome.
Received pack of 10 seeds today a little bit before time.This must be due to attentive sender and efficient postal system.The real test now falls to me to try to germinate ,transplant, and successfully grow even just one of the resulting plants and then I will be in a position to award even more stars.Thanks, from,Jerome.