
Pianta gigante (con frutti giganti)

















Il durian (noto anche con il nome di "durion"), italianizzato in durione, è il frutto degli alberi del genere Durio, soprattutto la specie Durio zibethinus, appartenente alla famiglia delle Malvaceae. Il nome di
Il durian (noto anche con il nome di "durion"), italianizzato in durione, è il frutto degli alberi del genere Durio, soprattutto la specie Durio zibethinus, appartenente alla famiglia delle Malvaceae. Il nome di questo frutto deriva dal malese, precisamente dal termine duri (spina) + il suffisso nominale an, traducibile in italiano con "frutto spinoso".
Particolarità e diffusione
La zona d'origine di questi frutti è il Sudest Asiatico, che è del resto anche la regione in cui la loro coltivazione e vendita sono più diffuse. In queste zone il durian è molto apprezzato, e l'appellativo che si è guadagnato presso le popolazioni locali è "re dei frutti". Il frutto di alcune specie emana un caratteristico odore, forte e penetrante anche quando il frutto è ancora chiuso, mentre altre specie sono inodori. Sebbene il gusto sia gradevole, l'odore del frutto quando presente risulta molto pungente e invade spesso le città della parte d'Asia in cui è diffuso, tanto che a Singapore, in Malesia e in Thailandia le autorità hanno esplicitamente vietato di introdurre i durian sui mezzi di trasporto pubblici.
Utilizzo in cucina
Nel continente asiatico è abitualmente preparato con il riso, e in Cina è impiegato in pasticceria. La polpa cremosa del durian può anche essere mangiata al naturale, oppure aggiunta al gelato o allo yogurt. I semi sono commestibili e, tostati o grigliati, si prestano a venir consumati come le noci.
Forma e dimensioni
Il frutto può arrivare ad assumere una lunghezza di 30 centimetri e un diametro di 15, mentre per quanto riguarda il peso, se quello medio oscilla tra 2 e 3 chilogrammi, esistono esemplari che arrivano a pesarne anche 5. Il durian ha forma ovoidale o tondeggiante, ed esternamente presenta una buccia dura, di colore verde o marrone, ricca di spine piuttosto spesse. All'interno si trova la polpa, che può avere un colore giallo pallido o rossastro, a seconda della specie. L'interno è suddiviso in sezioni, separate da una membrana non commestibile.
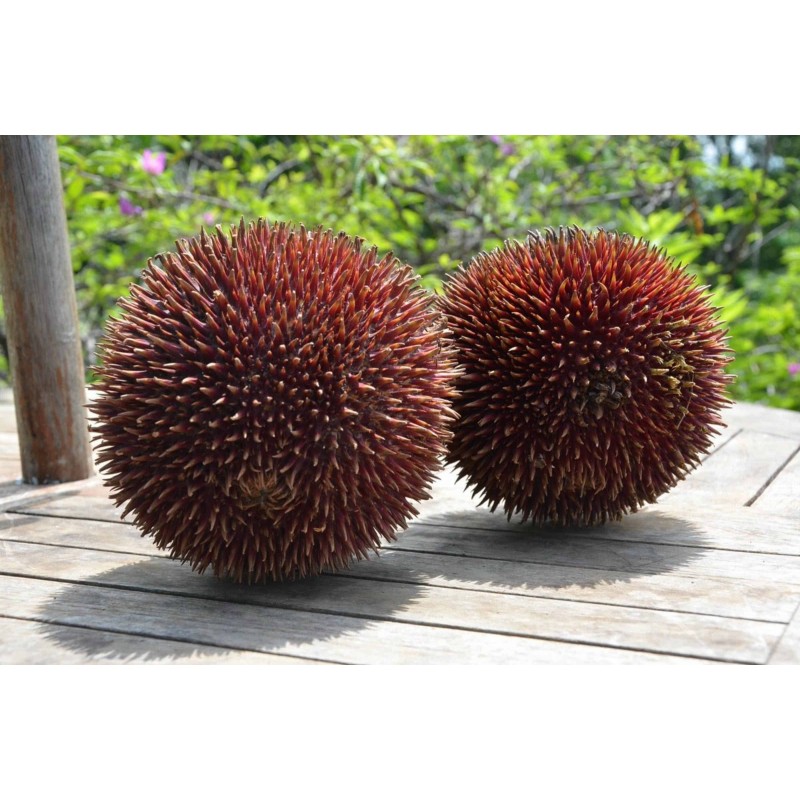
Everything about Durio dulcis is just a little bit magical. The tree is one of the more rare durians, residing deep in the jungles of Borneo. When in season, the red orbs dot the leafy forest floor like fallen Christmas ornaments, that sensational red leaping out of the green foliage like a natural stop light. It’s the strongest smelling durian, and its odor is said to waft as much as a kilometer through the jungle.
Durio dulcis has a bright red exterior with long, extremely sharp thorns that are sometimes yellow or black on the tips. It is extremely difficult to open because it lacks the weakened seams running stem to tip that every other durian opens along. Getting into a Durio dulcis requires a machete. Generally, the fruit is simply whacked in half and the gooey flesh is scraped out with the fingers.
In the case of Durio dulcis, the old adage, “Smells like hell but tastes like heaven” is exaggerated. The smell of Durio dulcis is absolutely overpowering. Although Durio graveolens literally means the “smelly durian,” the odor of Durio dulcis has by far the strongest aroma, an intoxicating vapor of industrial glue, menthol, and sugar.
Various botanists seemed to have had a love-hate relationship with the fruit. Writes durian explorer Wertit Soegeng-Reksodihardjo, “A
fruiting tree may be smelled for miles around, and a ripe fruit kept in a room is unbearably nauseating, even for the durian lover. Yet the pulp is most tasty and sweet.”
Regardless of opinions of smell, everyone agrees that in flavor Durio dulcis is unparalleled. The flesh is soft, almost soupy yellow draped loosely on large, nearly black seeds. It is the sweetest of the durians, like powdered sugar whipped into yogurt with a minty aftertaste. Anyone who likes mint chocolate will love this durian.
Distribution
It grows wild throughout Borneo, but is not generally cultivated. Rob and I found it twice; at the Agricultural Park in Tenom, Sabah, and near a longhouse in the Upper Kapuas region of West Kalimantan.
Local Names
Durio dulcis is known by a variety of names.
Here are some that we found: Durian Lai, Durian Tahi (Poop durian, may be a joke), Lahong, and Durian Merah (Red Durian. This can be also refer to the red-fleshed durio graveolens). Durian Api, Fire Durian.
Others have mentioned: durian bala (Kenya), Pesasang (tidung), durian isang (fish gill) and Durian Hutan (jungle durian).
Scientific Name
Durio dulcis literally means the “sweet durian” in Latin. It was named by the great botanist Odoardo Beccari during his three year exploration of Borneo between 1865-1868. He first found this durian during a stay on Mattang Mountain, near Kuching Sarawak. It was that odor that drew him to the right spot. He says, “attracted by the sweet and delicious scent exhaled by some fallen fruits, I discovered one of the most exquisite wild durians of Borneo, Durio dulcis.”
Despite its excellent flavor and the unabashed enjoyment by durian lovers, Durio dulcis is only occasionally cultivated. It is not considered of economical interest and hasn’t been the subject of much research. The tree is large, at least 40 meters tall, and the flowers are a lovely shade of pink. Like most other durians, it is naturally found in mixed lowland dipterocarp forests in both swampy areas and ridges up to 800 meters altitude. It is a robust tree and it has been suggested to use it as rootstock in commercial durian farming.
Temperature:
Durian is surprisingly tolerant of relatively low mean temperatures. There are places on the island of Java between 400-600 m [1300-2000 feet] altitude where durian is successfully grown that have a mean yearly normal temperature of just 23º C. (73º F.) Some research has indicated that growth is limited below a mean monthly temperature of 22º C. [71º F.]. The trees may survive occasional dips in temperature as low as 10º C. [50º F.], but may drop their leaves. On the other end of the spectrum, durian trees in India sometimes successfully tolerate high temperatures up to 46º C. [114º F.].
Water:
Durian trees need abundant rainfall, or equivalent irrigation. In most areas of Asia where durians are grown, mean annual rainfall is greater than 2000 mm [75 inches]. Historically, though, the better production sites have developed in areas with annual mean rainfall totals of 3000 mm [125 inches] or more, well distributed throughout the year. There is no doubt, though, that drier zones can produce good crops with appropriate irrigation. In India, durian trees are often planted along the banks of streams, where the roots can reach water. They do not do well very close to the ocean, having almost no tolerance for salinity in the soil.
Soil:
Durian trees grow best in a rich, deep, well-drained sandy clay or clay loam (deep alluvial or loamy soil), high in organic matter, pH range of 6 - 7. Heavy clay soils are not supportive of good durian tree growth and health, as they do not drain well. Seedlings make more vigorous growth when potted into media that is light and sandy rather than high in clay content.
Scheda tecnica
 Recensioni (0)
Recensioni (0)